How does the human body process CBD? CBD and the Body – Cannabinoids (found in the cannabis plant) are chemicals that trigger the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors in the brain and body, known as the Endocannabinoid System. This combined system of receptors creates the stable homeostasis that balances basic functions of the human body.
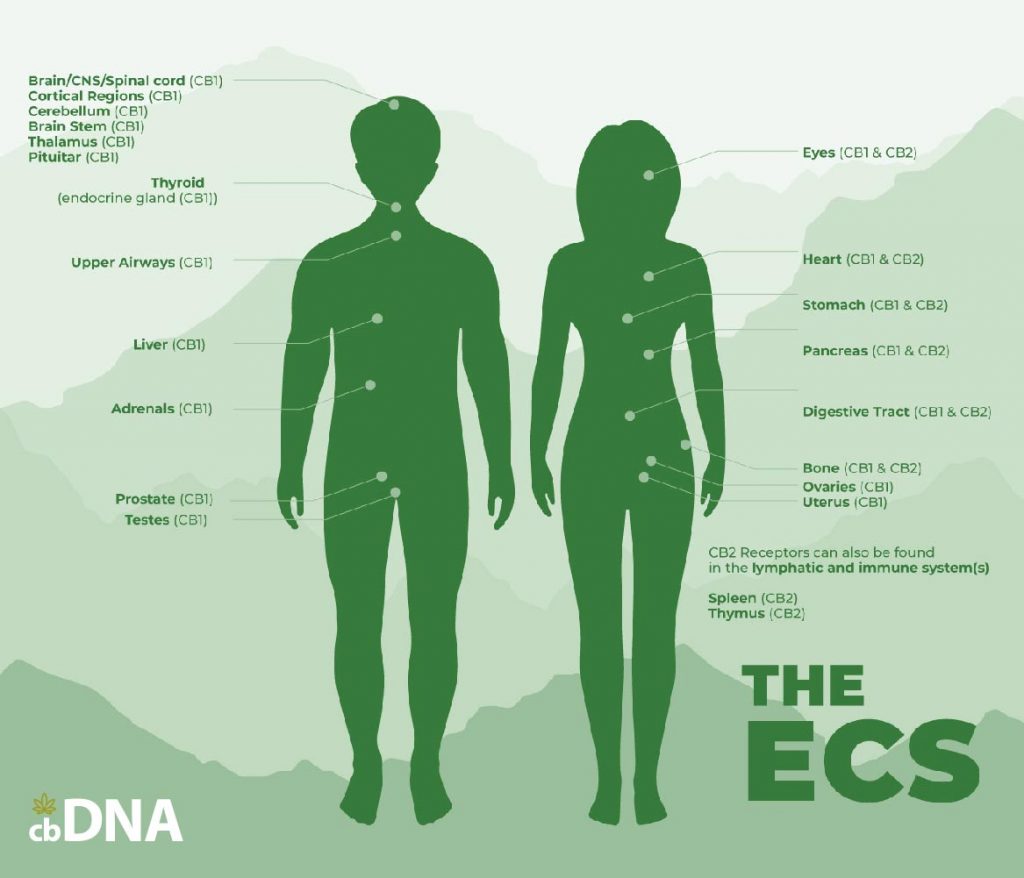
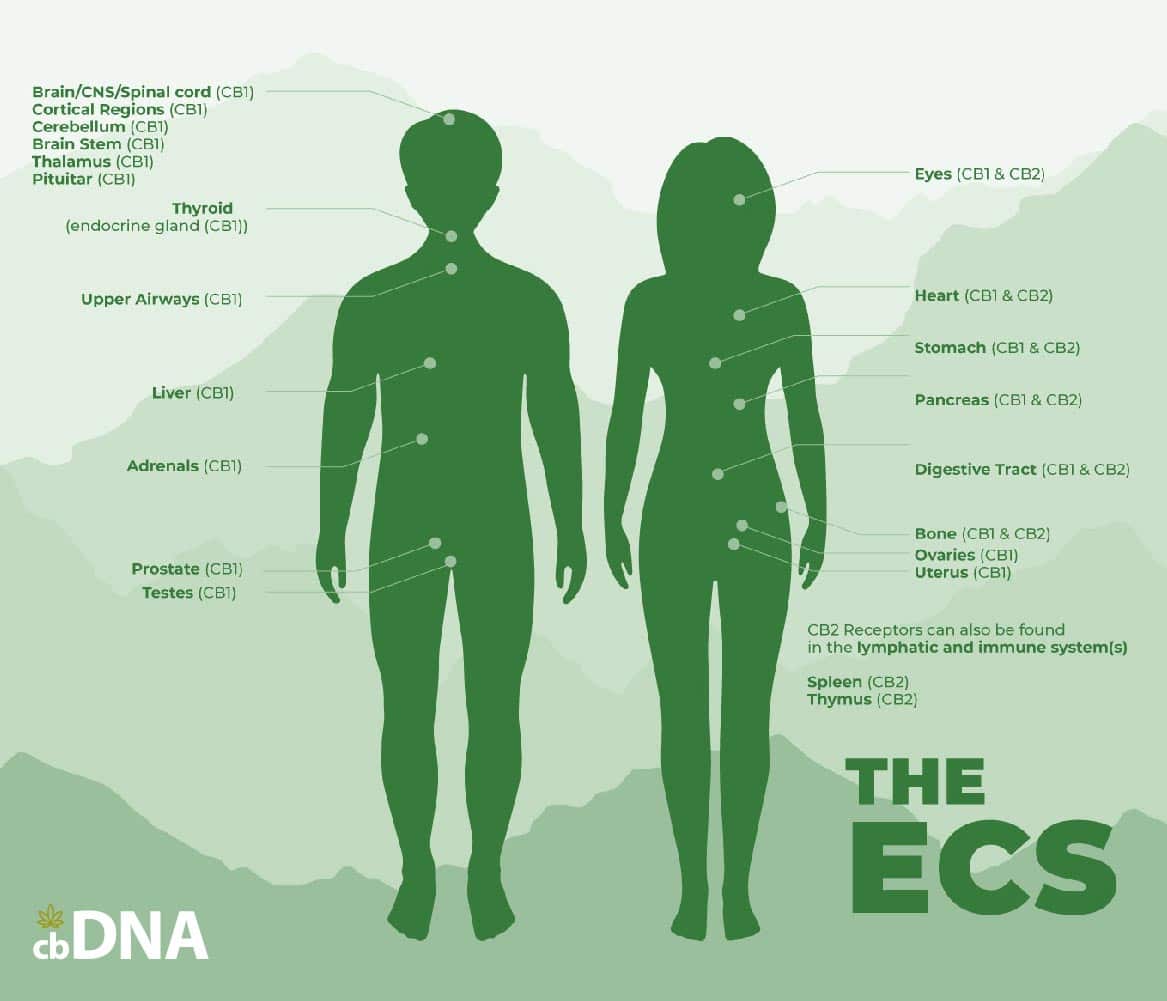
Cannabinoid Receptors
All mammals on this planet have an innate system on their bodies responsible for metabolising cannabinoids: the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). It was part of the discoveries of a 1960s study, as a result of deeper research and investigations about the Cannabis sativa plant and the effects it has on the body.
The cannabinoid receptors are responsible for detecting any changing conditions in the body. The two primary receptors are CB1 and CB2. CB1 works in the brain and nervous system and is responsible for processing the effects in the brain (like the reduction of anxiety or a high in the case of THC). CB2, which is in our tissues, organs, and the immune system, is responsible for the musculoskeletal benefits and/or any calming sensation we feel on our bodies.
Our Endocannabinoid System also produces enzymes called endocannabinoids, responsible for maintaining the balance of our bodies and regulating things such as our mood, appetite, sleep schedule, pain reception and more. We synthesize, or produce, the endocannabinoids whenever there are changes in the body. We bind them with the receptors to respond to such changes and regulate the conditions in our body.
CBD Oil and our ECS
Sometimes our Endocannabinoid System fails to work properly. When it does, we tend to feel out of balance. This is because we are not producing enough of the endocannabinoids enzymes that regulate our body functions.
The cannabinoids we ingest from the consumption of cannabis products interact with our receptors very similarly as the ones we produce ourselves. THC tends to bind with the CB1 receptors located in the brain, resulting in the psychoactive effect of being high.
However, CBD works a little differently. Instead of binding directly to our receptors, it stimulates the production of endocannabinoids in our body. The endocannabinoids, then, can be responsible for regulating it.