How to maintain your homeostasis? When our bodies become deficient in certain nutrients and vitamins, we eventually. The balance within our body also known as our ‘homeostasis’ will be thrown out. When this happens, our immune system and nervous system are not functioning properly. Which leads to inflammation, disease, and ultimately bad health.
Rebalancing your homeostasis before the disease is allowed to flourish within your body means you have to spot it. The signs of disease develop at an early stage and work on your diet. What nutrition and vitamins your body is being starved of?
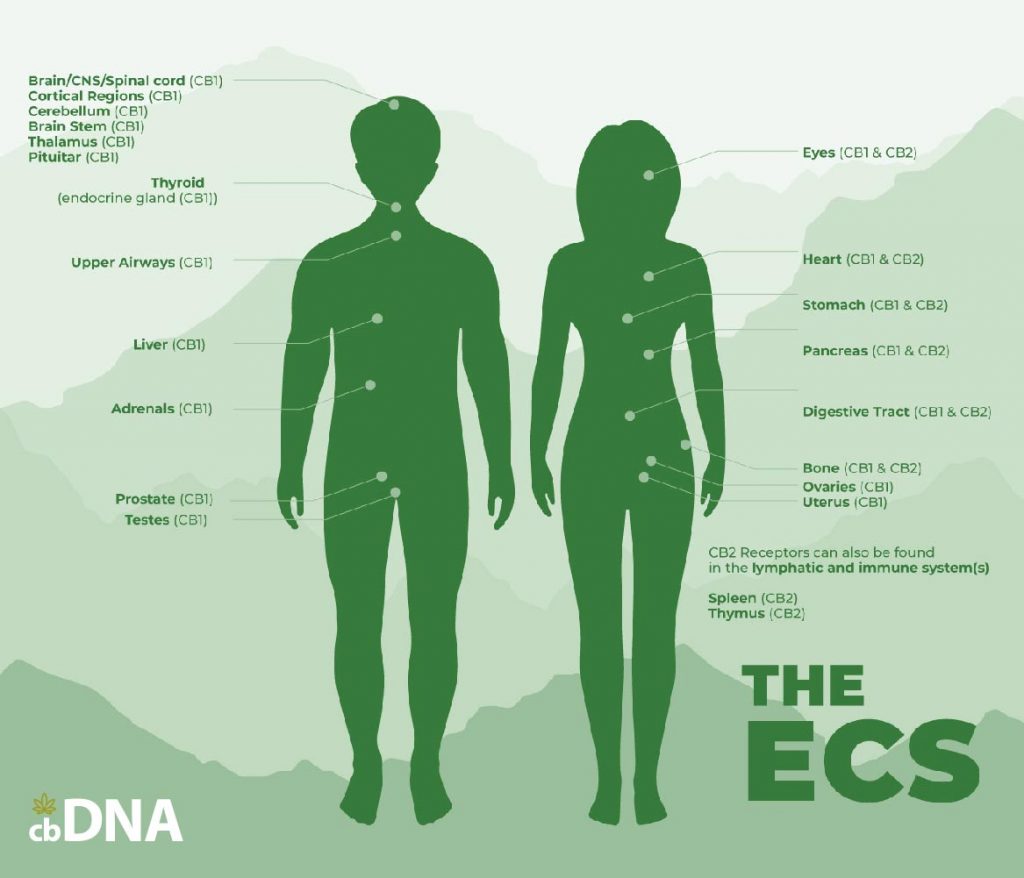
Your endocannabinoid system protects your homeostasis with a normal level of cannabinoids within our ECS. These are found in many different food sources. If you do not have a varied diet. Your cannabinoid levels can drop leading to a breakdown of your homeostasis and ultimately inflammation within the body. That will eventually lead to disease. If you are starting to have symptoms of inflammation and get on top of it early. With a change of diet add the nutrition needed to stave off illness. Also, top up your depleted endocannabinoid system. The cannabis plant is rich in cannabinoids, 108 to be exact.
The full spectrum of cannabinoids is preferable to get your endocannabinoid system working to optimum levels. It is possible to get this into your body through the use of full-spectrum CBD. Taking the right amount of full-spectrum CBD will allow your ECS to work. Alongside your immune system to rebalance your homeostasis. Just taking CBD alone will not fix your underlying nutritional deficit. You also need to assess your diet and work out which nutrients and vitamins your body is deficient in. Once you have the balance right and continue to take full-spectrum CBD, your health should return.
Maintaining homeostasis
Biological systems like your body are constantly being pushed out of their equilibrium points. For example, when you exercise, your muscles increase heat production, which increases your body temperature. Similarly, if you drink a glass of fruit juice, your blood glucose level will increase. Homeostasis depends on your body’s ability to recognize and counter these changes.
Maintaining homeostasis often involves negative feedback loops. These loops work in opposition to the stimulus or stimulus that activates them. For example, if your body temperature is too high. The negative feedback loop will bring it back to the setpoint or target value, which is 37.0C
How does it work? First, a high temperature is detected by sensors. Mainly nerve cells that line the ends of your skin and brain. And are relayed to your brain’s temperature control center. The control center processes the information and activates effectors – such as sweat glands. Whose job is to counteract the stimulus by lowering body temperature.
Homeostatic responses in temperature regulation
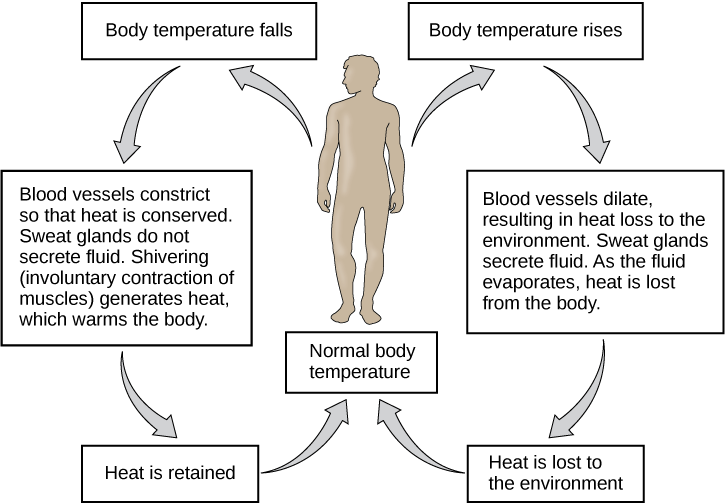
When you’re too hot or too cold. Sensors in your periphery and brain tell your brain’s temperature. Regulating center—an area called the hypothalamus—where your temperature is deviating from a set point. For example, when you exercise a lot, your body temperature can rise to a set point. You have to activate mechanisms to keep you cool. Blood flow to your skin will increase to speed up the loss of heat to your surroundings. And you may also begin to sweat, so the sweat evaporates from your skin to cool you down. Heavy breathing also increases heat loss. Figure showing temperature regulation in response to signals from the nervous system. When body temperature drops, blood vessels constrict, and sweat glands do not produce sweat. And vibrations generate heat that warms the body.
This ensures that heat is maintained back to normal body temperature. If the body temperature is too high. The blood vessels dilate, sweat glands release fluid, and heat is lost from the body. Once the heat from the surrounding environment dissipates, the body temperature returns to normal. Figure showing temperature regulation in response to signals from the nervous system. When body temperature drops and blood vessels constrict. Also, sweat glands do not produce sweat, and vibrations generate heat that warms the body. This ensures that heat is maintained back to normal body temperature. If the body temperature is too high and blood vessels dilate. The sweat glands release fluid, and heat is lost from the body. Once the heat from the surrounding environment dissipates, the body temperature returns to normal.
Image Credit: Homeostasis: Image 4 by OpenStax College, Biology, CC BY 4.0 On the other hand. If you are sitting in a cold room and are not warmly dressed. The temperature center of the brain must trigger reactions to help you warm up. Blood flow to the skin decreases and you may start to shiver so your muscles can generate more heat. You can also get goosebumps. So your body hair stands up and a layer of air gets close to your skin. And increase the release of hormones that work to increase heat production. CBD Homeostasis