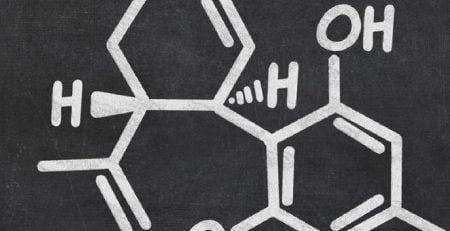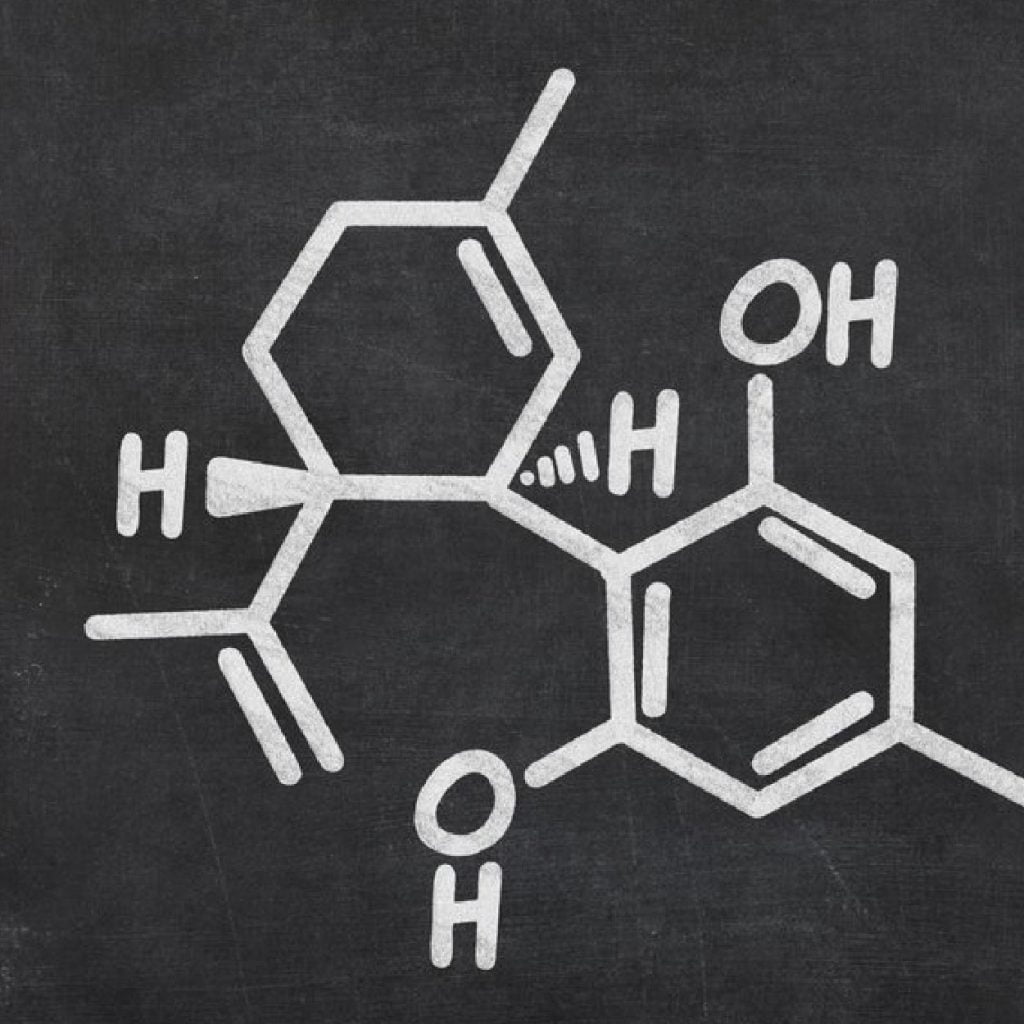
CBD Explained: Short for cannabidiol, is a chemical compound found in the Cannabis Sativa plant, of which Hemp is a variety. CBD is a type of cannabinoid, of which there are many found in Cannabis Sativa. It is non-psychoactive, which means it won’t get you high. The compound that causes the high from cannabis, THC, is only found in trace amounts in hemp. Pure CBD is legal, unlike THC, which is a controlled substance.
CBD products vary widely; the most common forms are oils, sprays, and vapes. It’s also available as a topical cream or muscle balm.
CBD’s actual effect on the human body is thought to affect our cell-signaling system (the endocannabinoid system), which helps to regulate functions such as sleep, immune response, and pain. This explains CBD’s potentially wide-ranging application. So, here’s CBD Explained
What can CBD be used for?
CBD is popular for a wide range of conditions, such as:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Eczema
- Arthritis
- Insomnia
- IBS
- Muscle Spasms
In addition to the above, there are many other conditions and ailments that It has been taken for.
Dosage-wise, It is something where you need to slowly and steadily increase your dosage until you reach the desired effect.
Detail
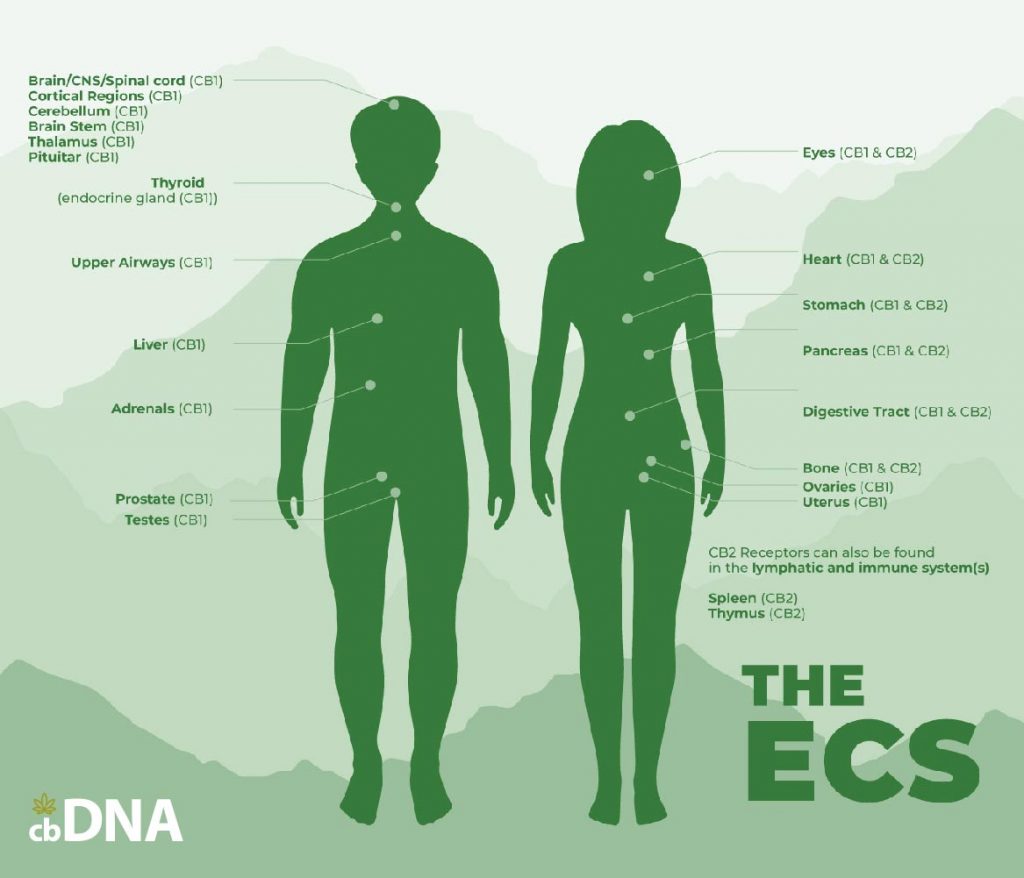
CBD and THC interact with our bodies in a variety of ways. One of the main ways is by mimicking and augmenting the effects of the compounds inour bodies called “endogenous cannabinoids” – so named because of their similarity to compounds found in the cannabis plant. These “endocannabinoids” are part of what scientists refer to as the “endocannabinoid system.”
The discovery of the endocannabinoid system has significantly advanced our understanding of health and disease. It has major implications for nearly every area of medical science and helps to explain how and why CBD and THC are such versatile compounds – and why cannabis is such a widely consumed plant, despite its illegal status.
The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating a broad range of physiological processes that affect our everyday experience – our mood, our energy level, our intestinal fortitude, immune activity, blood pressure, bone density, glucose metabolism, how we experience pain, stress, hunger, and more.
How is CBD extracted?
CBD oil is extracted from the resinous trichomes of cannabis plants. There are many different cannabis “strains” or varietals. The amount of present in the trichomes will depend on the particular variety of cannabis or hemp. Low-resin industrial hemp, which is legally defined as cannabis with less than 0.3 percent THC by dry weight, has fewer trichomes – and therefore less oil – than high-resin cannabis varietals.
But most high-resin cannabis strains these days are THC-dominant with little CBD. So choosing the appropriate CBD-rich cannabis chemovar, a variety of cannabis defined by its chemical constituents, is key for extracting CBD oil.
Trichomes are fragile structures that easily break off from the cannabis flower. Even rough handling is enough to shake off the trichomes. Making hashish or “kif” (hashish powder) involves manually removing the resinous trichomes by agitating the flower. Sometimes heat or pressure is applied to partially melt the trichomes together, turning the resin into a congealed slab, referred to as rosin, which can be smoked or ingested.
In addition to the resinous trichomes concentrated on the flowers and to a lesser extent on the leaves of the cannabis plant, there are the tiny sessile trichomes, which dot the stalk, but these contain hardly any oil or CBD. (Shaped like tiny inverted commas, non-glandular hairs without oil also cover the plant’s surface.) It is also absent in the roots or the seeds of cannabis and hemp. Companies that claim they derive CBD from hemp stalks or hemp seeds are making false claims. CBD Explained