CBD, being a relatively new phenomenon, can be confusing at the best of times. Here’s our CBD Glossary of the most common CBD terms and their meanings.
CBD Glossary Cannabinoid
A cannabinoid refers to 113 known compounds. Found in the cannabis plant and activates the body’s natural cannabinoid receptors.
Cannabidiol
A Plant-derived, non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is used to help ease stress, anxiety, inflammation, or muscle and joint pain.
Cannabinoid Receptors
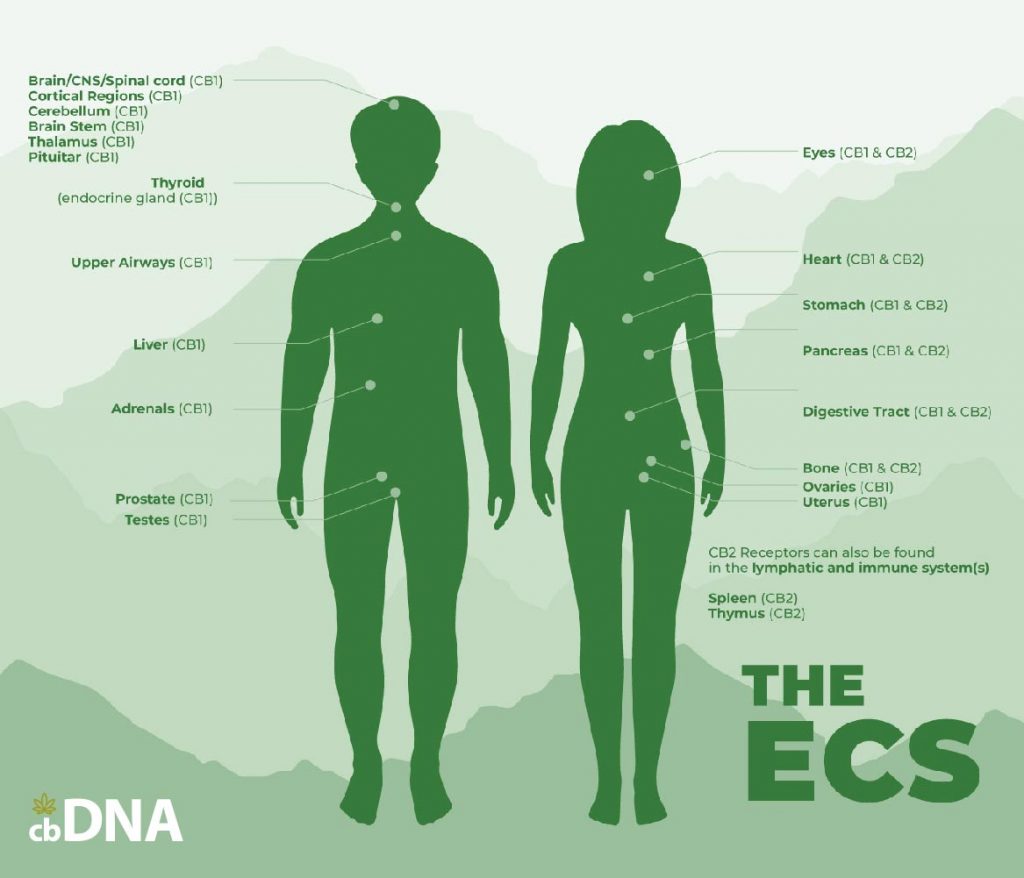
Found throughout the body as part of the endocannabinoid system. There are two sub-receptor groups: CB1 and CB2.
Cannabis
A breed of plant that includes marijuana (psychoactive) and hemp (non-psychoactive).
CBD Glossary
Hemp
Hemp is a plant in the cannabis family that contains a high concentration of CBD but less the 0.3% THC. It is what CBD for use in CBD products is extracted from.
Terpene
The natural, aromatic, and flavorful attributes of plant-derived essential oils. Terpenes provide unique fragrances and may heighten mood and reduce stress levels, particularly when combined with CBD and other cannabinoids.
CBD Glossary Full spectrum CBD
Full Spectrum CBD extract contains a wide range of terpenes and cannabinoids, including CBD CBG, CBN, and tiny amounts of THC.
CBD Isolate
CBD Isolate is a scentless and tasteless isolate that is at least 99% pure and contains no other compounds. Often mixed with a carrying oil and used in tinctures, drinks, and balms.
Endocannabinoid System CBD Glossary
The name for the biological system which is composed of endocannabinoids and receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It appears to work with the endocannabinoid system to help regulate the system.
CBD Glossary: Additional phrases to our main CBD Glossary above:
CBD Glossary Bioavailability
The bioavailability of CBD is the degree to which CBD (and other compounds) is absorbed by your system—the higher the bioavailability, the more CBD your body is able to utilize.
Co2 Extraction
A solvent-based extraction process that uses carbon dioxide in its supercritical state (above its critical point) for an efficient method for creating potent concentrates. Supercritical CO2 looks like a dense fog and has no surface tension, so it moves through vegetative material like a gas in a gaseous state yet it dissolves trichomes. A CO2 oil comprises of cannabinoids, terpenes, and waxes. CO2 is a tunable solvent, so different cannabinoids and terpenes can be targeted by changing the pressure and temperature of the extraction.
For a highly purified oil, scientists will put the CO2 oil through a distillation process to bring the cannabinoid content up to 85%+. This is the most expensive extraction method and is widely considered the most effective and safest plant extraction method in the world.
Distillate Oil
Distillate is a potent oil generated from a distillation process. This process uses heat to evaporate the volatile molecules in the biomass such as terpenes, THC, and CBD. After the molecules evaporate, they are cooled back down into a liquid oil while leaving behind all of the other plant matter. Distillate oil has the highest cannabinoid contents, with most oils containing above 85%. Since heat is used during distillation, the final oil has already been decarboxylated, so it can be infused into other products such as gummies. The most common forms of distillate on the market are THC oil and CBD oil.
Phytocannabinoids
The naturally occurring cannabinoids are found in the cannabis plant. There are 113 known phytocannabinoids in the cannabis plant, including CBD, CBN, THC, etc. CBD is a phytocannabinoid with the ability to mirror cannabinoids that the body produces itself (endocannabinoids). ‘Phyto’ is simply a prefix meaning “pertaining to derived from plants.” Most people refer to phytocannabinoids simply as cannabinoids.
We hope this CBD Glossary has been helpful in explaining CBD and its terms.